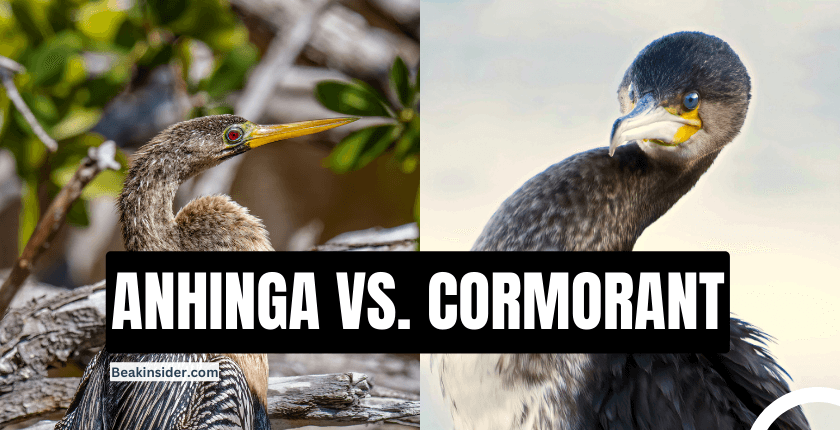
When it comes to the fascinating world of water-dwelling birds, two species that often capture our attention are the Anhinga and the Cormorant. These avian creatures possess unique characteristics and behaviors that distinguish them from one another.
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the key differences between Anhingas and Cormorants, shedding light on their physical attributes, habitats, feeding habits, and more. By exploring the distinct features of these remarkable birds, we aim to provide you with a deeper understanding of their individual traits and help you appreciate the diversity of the avian kingdom.
You may also like: Eagle Names
Physical Appearance
Anhinga
The Anhinga, scientifically known as Anhinga anhinga, is an elegant bird with a slender body and a remarkable wingspan of approximately four feet. It possesses a long, pointed bill, ideally suited for capturing prey in water. Anhingas exhibit sexual dimorphism, with males displaying glossy black feathers, while females have a brownish neck and a pale chest. Their elongated necks and serrated tail feathers are distinguishing features that contribute to their aerodynamic prowess.
Cormorant
Cormorants, belonging to the family Phalacrocoracidae, are slightly larger than Anhingas and showcase a robust build. These birds have a more compact wingspan, measuring around three to four feet. They possess a hooked bill that aids in catching fish and other aquatic prey. Cormorants exhibit similar sexual dimorphism to Anhingas, with males displaying darker plumage, while females have a lighter-colored neck. Their short, sturdy legs and webbed feet are adaptations that enable efficient swimming.
Main Difference in Physical Appearance
One of the most noticeable differences is the shape of their bills. Anhingas have long, pointed bills that are ideal for spearing fish underwater, while cormorants have hooked beaks that help them to grasp and hold onto slippery prey.
Another difference between these birds is their size. Cormorants tend to be slightly larger than anhingas, with wingspans of up to six feet in some cases. They also have longer necks and tails than anhingas do, which gives them a more streamlined appearance when swimming through water. Overall, while both birds share many similarities in terms of behavior and habitat preferences, it’s important to pay attention to these physical characteristics in order to tell them apart with confidence.
You may also like: Breeding Quaker Parrots
Differences in Habitat and Distribution
Anhinga
Anhingas predominantly inhabit freshwater environments, including marshes, swamps, and lakes, across the Americas. They can be found in regions such as the southeastern United States, Central America, and parts of South America. These birds prefer habitats with dense vegetation and ample water sources, where they can forage for fish and bask in the sun to dry their feathers.
Cormorant
Cormorants have a more extensive global distribution compared to Anhingas. They are found in both freshwater and marine habitats across the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia. These adaptable birds can be spotted near rivers, estuaries, coastal areas, and even on man-made structures such as docks and bridges. Cormorants are well-equipped to thrive in various environments, displaying remarkable versatility in their choice of habitat.
You may also like: Most Expensive Parrots
Differences in Feeding Behavior
Anhinga
Anhingas are primarily piscivorous, meaning their diet primarily consists of fish. They employ a unique hunting technique known as “daggering,” where they swim underwater, partially submerging themselves and using their sharp bills to spear unsuspecting prey. Anhingas possess a specialized adaptation that allows them to adjust their buoyancy, making them more agile underwater. After capturing a fish, they resurface, toss the prey into the air, and skillfully swallow it head-first.
Cormorant
Similar to Anhingas, Cormorants are skilled fishers. However, they employ a slightly different hunting strategy. Cormorants are adept divers, capable of reaching considerable depths to pursue their prey. They propel themselves underwater using their webbed feet and pursue fish with their powerful swimming abilities. Cormorants have specialized throat pouches that allow them to catch and store fish temporarily
Size, Shape, and Plumage Comparison
The Anhinga and Cormorant are both aquatic birds that share some similarities in their appearance but also exhibit some unique characteristics. In terms of size, the Anhinga is slightly larger than the Cormorant, with an average length of 35 inches compared to the latter’s 33 inches. The Anhinga also has a longer wingspan and tail feathers, making it more streamlined for aerial acrobatics.
In terms of shape, the Anhinga has a slender neck that is often held in an S-curve while swimming. This allows it to move quickly through the water without creating too much disturbance or drag. On the other hand, the Cormorant has a thicker neck that it uses to dive deep underwater and catch fish. Its body is more compact and streamlined than that of the Anhinga.
Finally, plumage comparison between these two species reveals some interesting differences as well. Both birds have black feathers on their backs and wings but differ in their underparts’ coloration. The Anhinga has white patches on its chest and belly while retaining its black crest on top of its head throughout all seasons. In contrast, during the breeding season (spring-summer), Cormorants develop white plumes on their heads, and back feathers become iridescent green-blue-black hues with small white spots over them; non-breeding adults have dark brownish-grey backs with paler undersides.
Difference in Habitat and Range
Habitat and range are important factors to consider when differentiating between two similar species, such as the anhinga and cormorant. The anhinga is commonly found in freshwater environments, such as swamps, marshes, and slow-moving rivers across North and South America. In contrast, the cormorant can be found in both freshwater and saltwater habitats worldwide.
The range of these two bird species also differs. The anhinga’s natural range extends from southern Canada down to Argentina, whereas the cormorant’s range spans Europe, Asia, Africa, Australia, and the Americas. Despite their different ranges and habitat preferences, both birds share a similar ecological niche as fish-eating predators.
Overall, understanding habitat and range is crucial for distinguishing between closely related species like the anhinga versus cormorant. Examining these features along with other morphological characteristics like bill shape or feather coloration patterns can help identify which bird you are observing in its natural environment.
Where do They Live and Migrate?
Anhingas are found in parts of North and South America, with their range extending from the southeastern United States to Argentina. They typically live in fresh or brackish water habitats such as swamps, marshes, and mangrove forests. Anhingas are non-migratory birds and tend to stay within their home range year-round.
Cormorants have a much wider distribution, living on every continent except Antarctica. They can be found in freshwater or saltwater habitats such as lakes, rivers, coastal areas, and estuaries. Cormorants are known for their long migrations; some species travel thousands of miles between breeding grounds and wintering sites.
Despite their different ranges and migratory habits, both anhingas and cormorants are adapted to aquatic environments and rely on fish as a primary food source. Their physical similarities – including elongated necks for underwater hunting – have led to confusion between the two species in the past.
Differences in Diet and Feeding Behavior
The anhinga and cormorant are two aquatic birds that can be found living in similar environments, but their diet and feeding behavior differ. Anhingas primarily feed on fish, while cormorants consume a wider variety of prey, including fish, crustaceans, and amphibians. Anhingas hunt by swimming underwater and impaling their prey with their sharp bill, while cormorants use their sharp beaks to catch and swallow their prey whole.
Another notable difference in feeding behavior between the two birds is how they dry off after diving for food. After hunting underwater, anhingas will perch with their wings spread out to dry them off before flying away. In contrast, cormorants have less waterproof feathers which allow them to dive deeper without getting weighed down by water. To dry off after diving for food or traveling long distances over water, cormorants will often stand with their wings spread out to absorb sunlight.
In summary, although both the anhinga and cormorant live in similar environments near bodies of water, they have different diets and feeding behaviors. The anhinga specializes in catching fish using its sharp bill while the cormorant consumes a variety of prey such as fish and crustaceans using its sharp beak.
Key Similarities, Differences, and the Importance of Conservation Efforts
Anhingas and cormorants are both aquatic birds that have similar body shapes and behaviors. They both have long necks, sharp beaks, and streamlined bodies that make them excellent swimmers. Anhingas are found in the Americas while cormorants can be seen all over the world.
Despite their similarities, there are also significant differences between anhingas and cormorants. The most noticeable difference is their feathers – anhingas have waterproof feathers only on their wings while cormorants’ feathers are entirely waterproof. This means that cormorants can dive deeper into the water for longer periods than anhingas.
The importance of conservation efforts for these species cannot be overstated as they play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our aquatic ecosystems. Both species face threats from habitat loss, pollution, overfishing, and hunting. Therefore it is essential to protect their habitats, manage fishing practices sustainably and prevent further pollution to ensure their survival for future generations to enjoy.
Conclusion:
Although anhingas and cormorants share several similar characteristics, they differ in their physical appearance, behavior, and habitat. Anhingas are slender birds with long necks that swim underwater to catch fish. In contrast, cormorants have shorter necks and dive deep into the water to hunt for fish. Additionally, anhingas can be found in freshwater habitats such as lakes and rivers while cormorants are more commonly seen in saltwater environments.
Furthermore, while both birds have a strong sense of community and nest in colonies, their social behaviors differ significantly. Cormorants often engage in communal fishing where they work together to herd schools of fish towards shallow waters for easy capture. On the other hand, anhingas typically hunt alone or with just one other bird.
Overall, it is fascinating how two seemingly similar species like the anhinga and cormorant can have such distinct differences that make them unique from each other. Their contrasting features illustrate the vast diversity of life on our planet and highlight the importance of preserving different types of animal habitats for future generations to enjoy.
You may also like:
- Catchy Penguin Name Ideas
- Pionus Parrot Names
- Can Parrots Eat Mango?
- Can Parrots Eat Mango? Benefits & Nutritional Value
- Are Parrots Omnivores Herbivores, Or Carnivores?
- Reasons Why Are Quaker Parrots Illegal
- Are Parrots Omnivores Herbivores, Or Carnivores?

I’m Amna, and I absolutely adore birds, especially parrots. I’ve been immersed in the world of these colorful feathered friends for over 10 years. While I’m not a bird doctor, I’ve gathered a wealth of knowledge on how to care for and understand them.
My experiences extend to various bird species like parrots, macaws, cockatoos, canaries, and finches. In addition to my personal adventures with birds, I’ve dedicated time to volunteering at a local bird rehabilitation center.
My true passion lies in sharing what I know about parrots and birds with you. Through my articles, I aim to share the information you need to provide the very best care for your avian companions. So, let’s embark on this journey together and make your feathered friends’ lives as joyful and healthy as possible!